Text Transformations for Search Term Matching
Search terms may contain special characters, diacritics, case differences, or language-specific variations, while your indexed data may not (or vice versa). When building a search experience in SPARQUE Desk, you need to ensure that incoming search terms (keywords) can successfully match with the terms stored in your dataset.
To achieve this, SPARQUE Desk provides several text transformation blocks. These blocks help normalize both user search queries and dataset entries so they can match consistently.
Scenarios
For understanding why text transformations are needed, consider these scenarios:
- A user searches for “St.-Veit-Straße”, but your data only contains “St.-Veit-Strasse”.
- A user searches for “Busch-Jäger”, but your index contains “Busch-Jaeger”.
- A user searches for “John Smith”, but the data stores it as “Smith, John”.
Without transformations, these searches fail to match. By applying normalization steps, you ensure that both sides of the comparison use the same string representation.
Available Transformation Blocks
This section covers the text processing blocks you can use in SPARQUE Desk.
Normalize Diacritics
Purpose: Convert accented or special characters into their ASCII equivalent.
Example:
Nguyễn Tấn Dũng→Nguyen Tan DungSt.-Veit-Straße→St.-Veit-Strasse
This ensures that diacritics do not prevent matching when the dataset stores only plain ASCII versions. For details, refer to Normalize Diacritics.
Language Transliteration
Purpose: Handle language-specific transliterations for special characters.
Example (German):
ä→ae(Busch-Jäger→Busch-Jaeger)ö→oeü→ue
Example (Swedish):
å→aa(Håkan→Haakan)
This block is useful when your data follows language-aware spelling rules. For details, refer to Language Transliteration and Language Transliteration [Strings].
String Fingerprint
Purpose: Create a simplified “fingerprint” of a string by:
- Lowercasing
- Removing accents
- Tokenizing and sorting tokens
Example:
The Big House→bighousetheHouse, Big The→bighousethe
Both strings result in the same fingerprint, ensuring consistent matching regardless of word order or accents. For details, refer to String Fingerprint.
Change Case
Purpose: Standardize letter casing.
Example:
SPARQUE DESK→sparque desk(lower-case)sparque desk→SPARQUE DESK(upper-case)
This ensures case-insensitive matching. For details, refer to Change Case.
Stem
Purpose: Reduce words to their root (stem) form.
Example (English):
running,runs,ran→run
Example (Dutch):
lopend,lopen→loop
Stemming is especially useful when you want different inflected forms of a word to match. For details, refer to Stem.
Replace with RegEx
Purpose: Use regular expressions to replace text patterns. This is the most flexible block and can handle custom formatting issues.
Examples:
Normalize multiple spaces:
Pattern:\s+→ Replacement:" "John Smith→John SmithSwap names:
Pattern:^([^,]+)\s*,\s*(.+)$
Replacement:$2 $1Smith, John→John SmithExtract a day of the week (case-insensitive):
Pattern:.*\b((?:mon|tue|wednes|thurs|fri|sat|sun)day)\b.*
Replacement:$1Next Monday Morning→Monday
For details, refer to Replace with RegEx and Replace with RegEx [Strings].
Best Practices
When working with text transformations, consider the following best practices:
- Normalize both sides:
Apply transformations to both the incoming keyword and the dataset entries to ensure that they are comparable. - Keep transformations consistent:
If you lowercase the dataset terms, also lowercase incoming queries. - Use fingerprints for messy data:
If your data varies in order or spacing, use String Fingerprint. - Start simple, extend as needed:
Begin with Normalize Diacritics and Change Case. Add Transliteration, Stemming, or RegEx rules for specific use cases.
Example Workflow
- Transform the words from your dataset into normal characters. For example, apply Normalize Diacritics and Change Case.
- Repeat these steps for the incoming parameter (often keyword).
- Compare the transformed parameter against the transformed dataset terms.
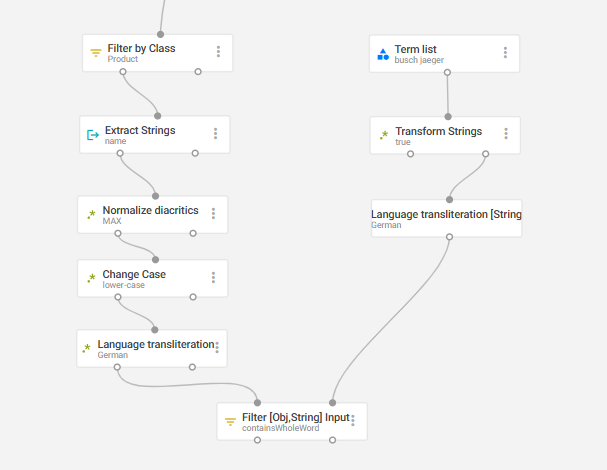
With these transformations, your SPARQUE Desk search engine can handle special characters, accents, cases, and language-specific spelling differences, leading to more accurate and user-friendly results.
